In the dynamic interplay of natural disasters, drought and earthquakes stand as two of the most challenging phenomena humanity faces. These events, though seemingly distinct, have a surprising number of interconnections that impact ecosystems, economies, and societies worldwide. While drought deprives regions of water and sustenance, earthquakes disrupt lives with their sudden and often devastating tremors. Together, they highlight the fragile balance of Earth's natural processes and the importance of understanding their underlying causes.
For centuries, people have grappled with the effects of these disasters, yet their origins and consequences remain elusive to many. Droughts are long-term events, often creeping into regions and leaving behind economic, agricultural, and environmental scars. Earthquakes, on the other hand, strike with little warning, shaking the ground beneath our feet and impacting infrastructure, ecosystems, and human lives. Their occurrence may seem independent, but scientific research suggests that shifts beneath the Earth's crust can influence water availability, and vice versa.
In an age where climate change exacerbates the frequency and severity of natural disasters, drought and earthquakes demand urgent attention. By delving into their causes, effects, and mitigation strategies, humanity can better prepare for these challenges. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate dynamics between drought and earthquakes, shedding light on their shared and unique characteristics while offering actionable insights to foster resilience against these phenomena.
Read also:Sudafed And Mucinex The Ultimate Guide To Relieve Congestion
Table of Contents
- Causes of Drought
- Types of Drought
- Impacts of Drought on the Environment and Society
- Causes of Earthquakes
- Types of Earthquakes
- Impacts of Earthquakes on the Environment and Society
- Interconnection Between Drought and Earthquakes
- Role of Human Activity in Exacerbating Drought and Earthquakes
- Climate Change and Its Influence on Natural Disasters
- Technological Advancements in Monitoring and Mitigation
- Mitigation Strategies for Drought and Earthquakes
- Global Examples of Drought and Earthquake Management
- Role of Governments and Communities in Disaster Preparedness
- Future Outlook: Reducing the Impact of Drought and Earthquakes
- Frequently Asked Questions
Causes of Drought
Drought, one of nature’s most prolonged and impactful disasters, arises from a combination of climatic, environmental, and anthropogenic factors. At its core, drought occurs when a region experiences a significant deficit in precipitation over an extended period. This lack of rainfall disrupts the water cycle, decreasing the availability of surface and groundwater resources.
Key drivers of drought include atmospheric patterns like high-pressure systems that block storm formation, El Niño and La Niña phenomena, and global warming. While natural processes play a significant role, human activities such as deforestation, unsustainable agricultural practices, and urbanization exacerbate the problem. Overextraction of groundwater and mismanagement of water resources further contribute to the growing severity of droughts worldwide.
Types of Drought
Droughts are classified into four primary types based on their causes and effects:
- Meteorological Drought: This occurs when an area experiences below-average precipitation, disrupting typical weather patterns.
- Hydrological Drought: Triggered by reduced water levels in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, often as a result of prolonged meteorological droughts.
- Agricultural Drought: Affects crop production and soil moisture, leading to food insecurity and economic challenges for farmers.
- Socioeconomic Drought: The most complex type, this results from a combination of the above droughts, impacting water supply, industries, and human livelihoods.
Impacts of Drought on the Environment and Society
The consequences of drought extend far beyond dry landscapes and water shortages. Environmentally, droughts lead to desertification, loss of biodiversity, and increased susceptibility to wildfires. Aquatic ecosystems also suffer, with reduced water flow disrupting the habitats of fish and other aquatic species.
Societally, droughts cause food and water insecurity, forcing communities to migrate in search of better living conditions. Economies reliant on agriculture and hydropower face significant setbacks, while public health deteriorates due to malnutrition and waterborne diseases. Additionally, the psychological toll on affected populations cannot be overlooked, as prolonged droughts create stress and anxiety.
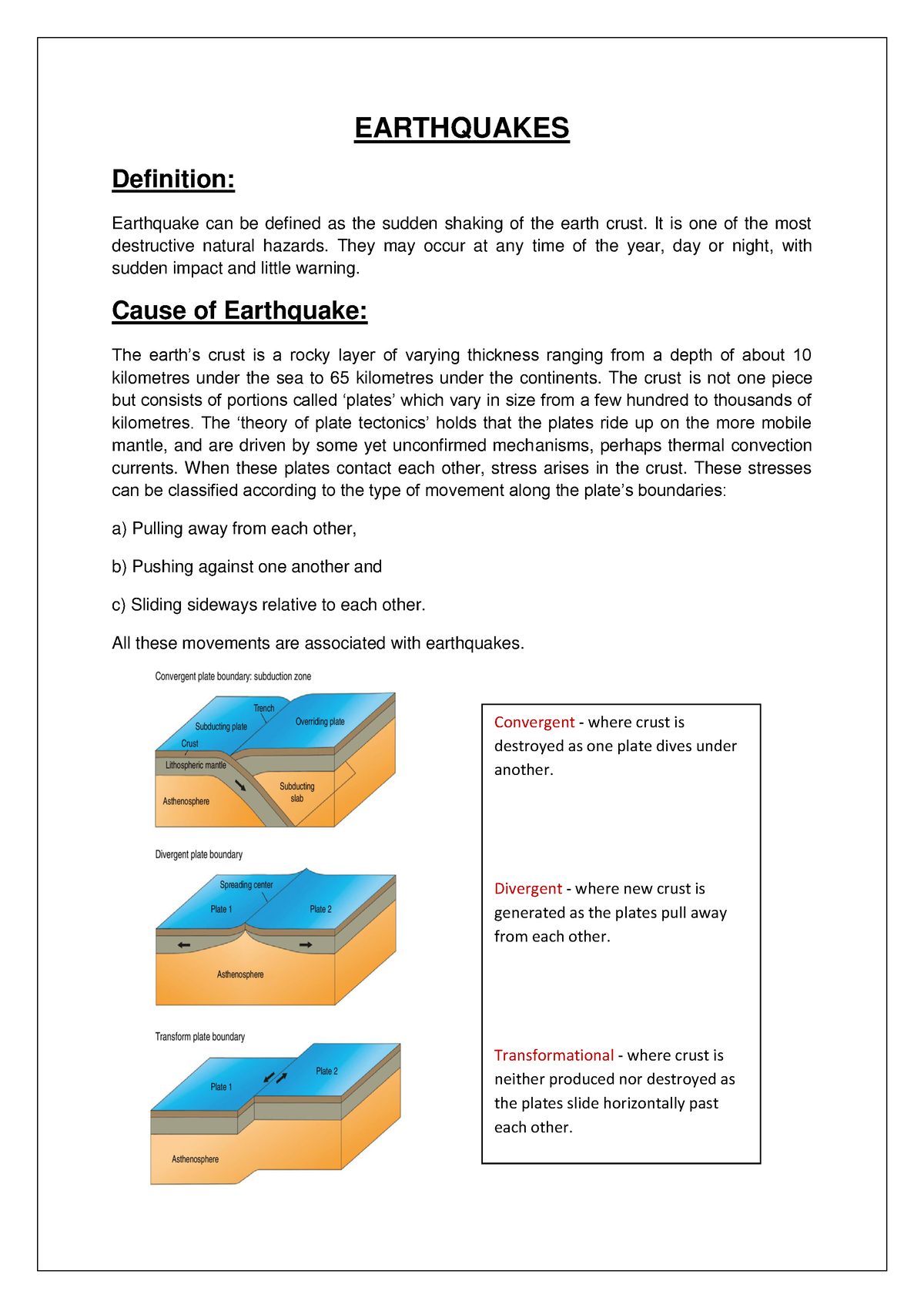
Causes of Earthquakes
Earthquakes are sudden tremors caused by the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface. These movements occur along fault lines, where energy builds up over time and is released as seismic waves. The primary causes of earthquakes include:
Read also:Hilary Duff Titties
- Tectonic Activity: The collision, sliding, or separation of tectonic plates, which creates stress along fault lines.
- Volcanic Activity: Magma movement and volcanic eruptions can trigger localized earthquakes.
- Human-Induced Activity: Activities such as mining, reservoir-induced seismicity (from dam construction), and deep well injections for oil and gas extraction.
Though unpredictable, understanding these causes helps scientists identify high-risk zones and develop early warning systems.
Types of Earthquakes
Earthquakes are categorized based on their origin and characteristics:
- Tectonic Earthquakes: The most common type, caused by the movement of tectonic plates.
- Volcanic Earthquakes: Associated with volcanic activity and magma movement.
- Collapse Earthquakes: Resulting from the collapse of underground caves or mines.
- Induced Earthquakes: Triggered by human activities, such as fracking or dam construction.
Impacts of Earthquakes on the Environment and Society
Earthquakes have far-reaching impacts on both the environment and society. The immediate effects include ground shaking, surface ruptures, and landslides. These physical changes alter landscapes, damage ecosystems, and disrupt natural water flow. In some cases, earthquakes trigger secondary disasters like tsunamis and fires.
On a societal level, earthquakes devastate infrastructure, displace communities, and lead to significant economic losses. The loss of life and injuries among affected populations creates long-term social and psychological challenges. Furthermore, rebuilding efforts require substantial resources and time, making recovery a slow and arduous process.
Interconnection Between Drought and Earthquakes
While drought and earthquakes may appear unrelated, their interconnection lies in the Earth's geophysical processes. For instance, prolonged droughts can reduce water pressure in underground aquifers, causing shifts in the Earth's crust that may trigger earthquakes. Conversely, earthquakes can disrupt water sources, exacerbating drought conditions in affected regions.
Research also indicates that human activities, such as groundwater extraction and reservoir construction, play a role in linking these phenomena. Understanding these interconnections is crucial for developing comprehensive disaster management strategies.
Role of Human Activity in Exacerbating Drought and Earthquakes
Human activities significantly influence the occurrence and intensity of droughts and earthquakes. Unsustainable practices, such as deforestation, urbanization, and overextraction of natural resources, disrupt the delicate balance of Earth's systems. Additionally, activities like fracking and dam construction alter the Earth's crust, increasing the likelihood of seismic events.
Addressing these challenges requires adopting sustainable practices, enforcing stricter regulations, and promoting global cooperation to mitigate human-induced disasters.
Climate Change and Its Influence on Natural Disasters
Climate change acts as a catalyst for natural disasters, intensifying the frequency and severity of droughts and earthquakes. Rising global temperatures disrupt weather patterns, leading to prolonged droughts in some regions and increased rainfall in others. These changes in water distribution affect groundwater levels and contribute to seismic activity.
Efforts to combat climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy, are essential for mitigating its impact on natural disasters.
Technological Advancements in Monitoring and Mitigation
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the way we monitor and mitigate natural disasters. Tools like satellite imagery, seismic sensors, and artificial intelligence enable scientists to predict droughts and earthquakes with greater accuracy. Early warning systems and real-time monitoring help communities prepare for and respond to disasters more effectively.
Investing in research and innovation is critical for developing new technologies that enhance our ability to manage natural disasters.
Mitigation Strategies for Drought and Earthquakes
Mitigating the impact of drought and earthquakes requires a multifaceted approach that combines prevention, preparedness, and response. Key strategies include:
- Implementing sustainable water management practices to combat droughts.
- Strengthening building codes and infrastructure to withstand earthquakes.
- Educating communities on disaster preparedness and response measures.
- Promoting international cooperation for resource sharing and knowledge exchange.
Global Examples of Drought and Earthquake Management
Countries worldwide have implemented innovative solutions to manage droughts and earthquakes. For example, Israel’s advanced water recycling systems address water scarcity, while Japan’s earthquake-resistant buildings minimize damage during seismic events. Sharing these success stories inspires other nations to adopt similar practices.
Role of Governments and Communities in Disaster Preparedness
Governments and communities play a vital role in disaster preparedness and recovery. Policies and regulations, combined with community engagement and education, create a resilient society capable of withstanding natural disasters. Collaborative efforts between public and private sectors further enhance disaster management capabilities.
Future Outlook: Reducing the Impact of Drought and Earthquakes
As the world faces an increasing number of natural disasters, prioritizing research, innovation, and collaboration is essential. By addressing the root causes of droughts and earthquakes and implementing effective mitigation strategies, humanity can build a more resilient future for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can drought trigger earthquakes?
Yes, prolonged droughts can reduce underground water pressure, potentially causing shifts in the Earth's crust that lead to seismic activity.
2. How does climate change exacerbate drought and earthquakes?
Climate change disrupts weather patterns, intensifying droughts and altering groundwater levels, which may contribute to seismic activity in certain regions.
3. What are the main human-induced causes of earthquakes?
Human activities like fracking, reservoir-induced seismicity, and deep well injections can trigger earthquakes by altering the Earth's crust.
4. How can technology help mitigate the impact of drought and earthquakes?
Technologies like early warning systems, satellite monitoring, and AI-based predictions enhance our ability to prepare for and respond to natural disasters.
5. What are the economic impacts of drought and earthquakes?
Both disasters cause significant economic losses by damaging infrastructure, disrupting industries, and affecting agricultural productivity.
6. What role can individuals play in disaster preparedness?
Individuals can contribute by staying informed, following safety guidelines, conserving water, and participating in community disaster preparedness programs.